- Home
- About Us
- Courses
- NSHM Business School
- BBA (Bachelor of Business Administration)
- BBA – Hospital Management
- BBA – Global Business
- BBA – Sports Management
- BBA – Accountancy, Taxation & Auditing
- BBA – Accountancy, Taxation and Auditing + BSE Certification
- BBA – Banking & Financial Services
- MBA (Master of Business Administration)
- Executive MBA
- MHA (Master of Hospital Administration)
- NSHM Institute of Health Sciences
- Bachelor of Pharmacy
- Bachelor of Pharmacy (Lateral)
- Bachelor of Optometry
- B.Sc. – Psychology
- B.Sc. – Dietetics and Nutrition
- B.Sc. – Medical Lab Technology
- B.Sc. – Radiology & Medical Imaging Technology
- B.Sc. – Critical Care Technology
- B.Sc. – Yoga
- Master of Optometry
- Master of Optometry(BL)
- Master of Pharmacy – Pharmacology
- Master of Pharmacy – Pharmaceutics
- Master of Public Health
- Master of Public Health (BL)
- M.Sc. – Clinical Psychology
- M.Sc. – Dietetics and Nutrition
- M.Sc. – Medical Lab Technology
- M.Sc. – Radiology & Medical Imaging Technology
- M.Sc. – Yoga
- M.Sc. – Yoga (BL)
- NSHM Design School
- NSHM Institute of Computing & Analytics
- NSHM Institute of Engineering & Technology
- B. Tech. – Mechanical Engineering
- B. Tech. – Mechanical Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. in Civil Engineering
- B. Tech. – Civil Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Computer Science Engineering
- B. Tech. – Computer Science Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Electronics & Communication Engineering
- B. Tech. – Electronics & Communication Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- B. Tech. – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Electrical Engineering
- B. Tech. – Electrical Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Data Science
- B. Tech. – Data Science (Lateral)
- NSHM Institute of Hotel & Tourism Management
- NSHM Institute of Nursing
- NSHM Media School
- NSHM Business School
- Schools & Campuses
- Beyond Academics
- Admissions
- News & Events
- Contact Us
Our Campus
With 2 sprawling state-of-the-art campuses in Kolkata and Durgapur, we ensure that our students have access to the best of educational facilities that are at par with international standards. Both campuses are replete with new age classrooms, recreational zones, modern student laboratories with the latest equipment and practicing tools, and an environment that fosters a vibrant culture that is conducive to bringing out the best in our students.
Our Legacy
25 +
Years of Academic Excellence
35000
Strong Alumni Network
500 +
Industry Associates
65 +
Professional Degree Programmes
Academic Excellence at NSHM
- Extended Learning
- Knowledge Partners
- Research


Choice Based Extended Learning
The choice-based extended learning (CBEL) programme, which unites NSHM students from various programmes & levels (undergraduate to graduate), according to their preferences, is an innovative offering by NSHM with 50+ CBEL programmes, each lasting 20–40 hours & divided into 10 baskets. The baskets are loaded with carefully chosen, multidisciplinary learning opportunities facilitate active learning.


Knowledge Partners
NSHM has partnerships with numerous apex organisations in a variety of fields that are each knowledge hubs in their own right. Students now have access to cutting-edge Industry Exposure in pertinent fields, which enriches their overall learning experience. Students gain skills and in-depth knowledge through workshops, training, etc that assist to shape them into professionals who are ready for the workplace.


Research
The NSHM’s Research division further fuels the goal of academic excellence. Faculty members conduct research projects that are supported by both public and commercial organisations. Students are also included to help with research. Their knowledge base is enhanced, and their ability to think critically and analytically is developed, which eventually carries out the contribution to the institute’s academic programme’s better standards.
NSHM Life Skills School
The 6 NSHM Life Skills School at NSHM Knowledge Campus are committed to contribute towards the holistic development of the students by nurturing their talents through unique programmes and initiatives which are devised and carried out by experts.
Student Services
Our Campus Life
Placements
-

Placement
-

Highest Package
-

Average Salary
Student Service Cell
-

Career Support
-

Administration & ITES Support
-

Examination & University Affairs
-

Admission & Academic Advise
-

Financial Counsel
International
Students
- PRE-ARRIVAL SUPPORTS
- ORIENTATION PROGAMME
- ONGOING SUPPORT
- STUDENTS FROM BANGLADESH
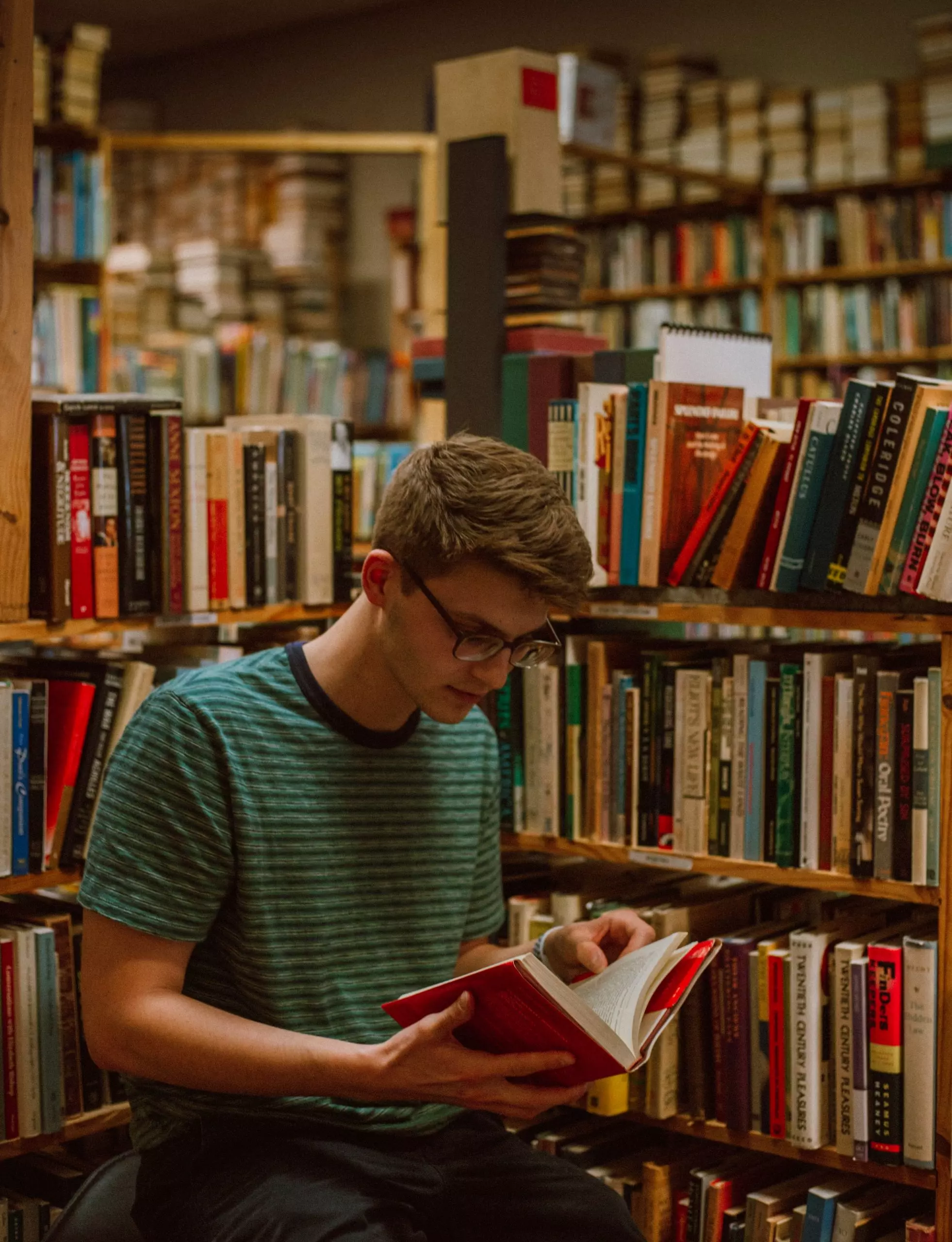

Providing assistance from the onset
The college offers a range of pre-arrival services to international students, including orientation materials, housing support, and cultural integration resources, to ensure a comfortable adjustment to campus life. These services seek to improve the overall experience for our international student community by ensuring a smooth arrival and facilitating a successful academic journey.
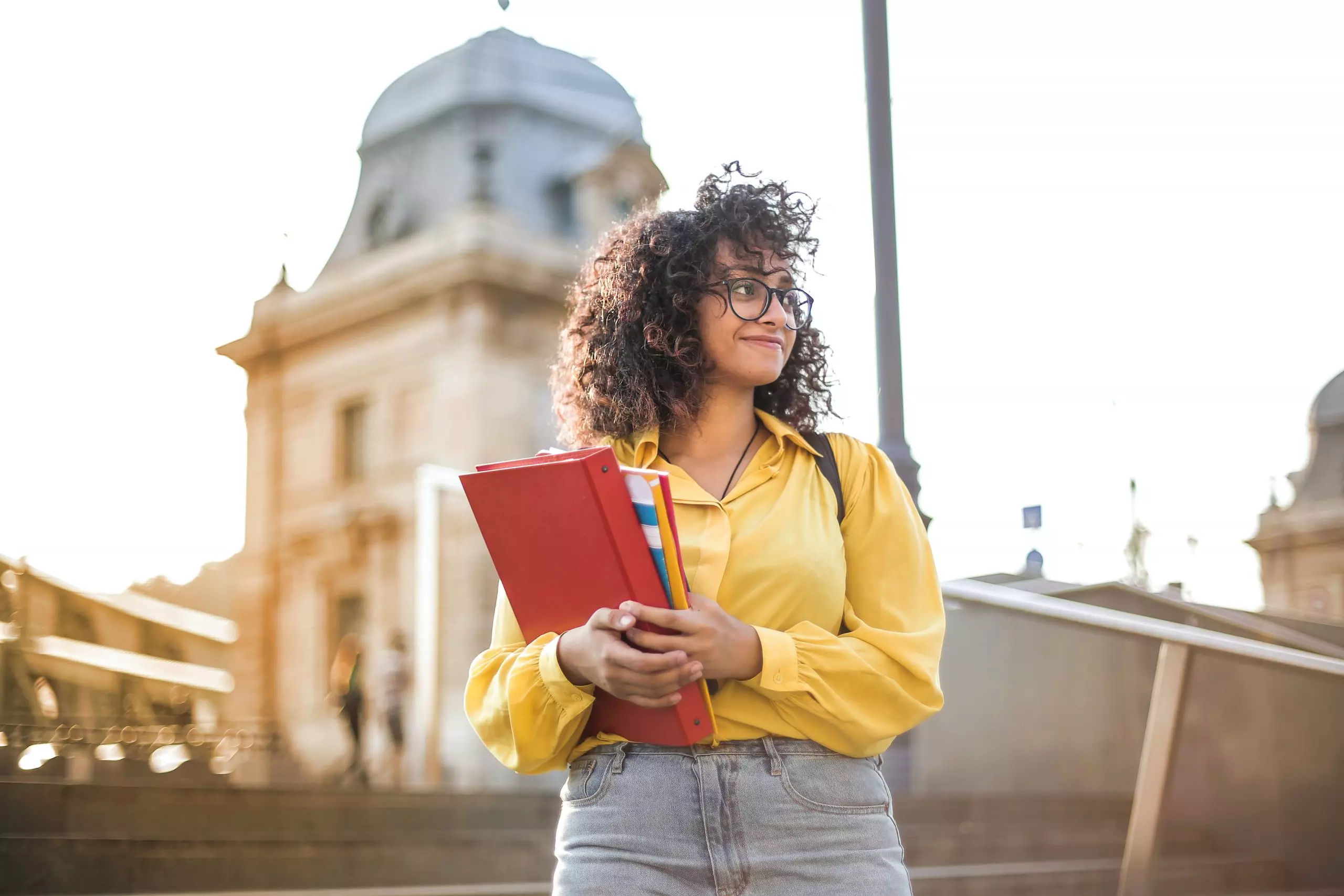

Ensuring a smooth transition
Organized for our overseas students, this programme is to help them adjust to their new surroundings, grasp academic expectations, and become acquainted with campus facilities. It is intended to establish in them a sense of belonging and assist in their academic and personal endeavours while studying abroad.

Round the clock service
NSHM prioritises continual support for overseas students with a cell that is 24 x 7 in operation. Dedicated advisors help students with academic and personal issues, ensuring a smooth integration with the school community at large. The friendly environment in the campus promotes inclusivity and global viewpoints in order to provide a successful and meaningful educational experience.
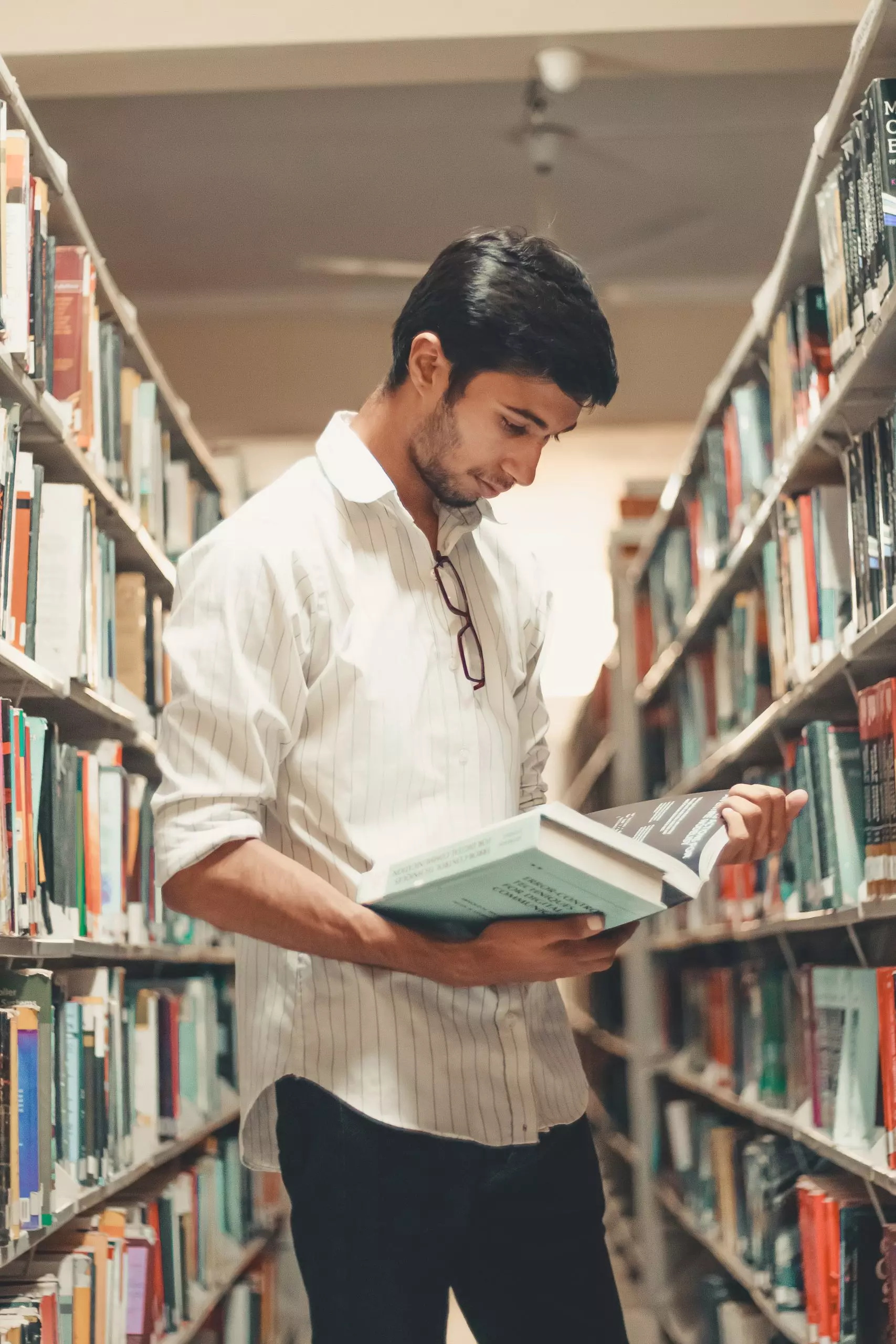

Hassle-free paperwork facilitated
Our dedicated team provides guidance on legal requirements, ensuring students can focus on their studies without facing bureaucratic hurdles. We strive to create a welcoming environment by addressing documentation needs efficiently and effectively.
What's Happening at NSHM
Blog
By NSHM | May 8, 2024
Why Choose NSHM for BCA Course
The BCA program has been a cornerstone offering at NSHM Knowledge Campus, Kolkata since 2006. Renowned for its academic excellence and student achi...
Read More
By NSHM | May 7, 2024
Exploring Career Opportunities in Dietetics and Nutrition
The area of nutrition and dietetics has expanded significantly in recent years due to growing public awareness of wellness, health, and the critica...
Read More
By NSHM | May 6, 2024
Exploring the World of Film Studies at NSHM Media School
Movies have been a part of our lives for over a century now, and they have become an art form that holds a significant place in our culture. Films ...
Read More